Database and Database-Management System
What is Database?
A database is an organized collection of data.
What is Database-Management System?
A database-management system (DBMS) is a computer-software application that interacts with end-users, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data. A general-purpose DBMS allows the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases.
Why do we need Database?
We need to store some data set, a list of events with id, name, address, and date. What will you do? Text File? Excel?
- The size of list is large( > 1 million users).
- Add some constraints to some data, such as ID of each user should be different.
- Create relations between different kind of data, such as users saved some events before.
- Quickly retrieve data based on given condition, such as retrieve all events happened in San Francisco.
- Quickly update or delete data based on given condition, such as update all favorite events for a given user.
- Need access control on the data, meaning only authorized users can have access to the data set.
- Allow multiple users access(add, search, update, delete) the data set at the same time.
A DBMS allows you to fulfill all requirement above easily.
Create our database by using MAMP
MAMP stands for “My Apache, MySQL, and PHP”. MAMP is an integrated platform you can install on your machine which allows you to have access to a local MySQL server and its PHP server.
Click Preferences -> Ports. Make sure Apache Port is 8888 and MySQL port is 8889. Don’t worry about the Nginx port.
Start Server->open phpMyAdmin->create new project myproject->use utf8_general_ci as the collation
Relational DBMS
ER (entity-relationship) model:
- Entity
- Relation: connect different entities
MySQL
Basic Concepts
- Table: a collection of attributions. Similar to what you’ve seen in an excel chart. Each column is an attribute of an entity, and each row is a record/instance of an entity.
- Row: a single, implicitly structured data item in a table
- Column: a set of data values of a particular simple type, one for each row of the table
- Schema: blueprint of how table is constructed.
Project Structure
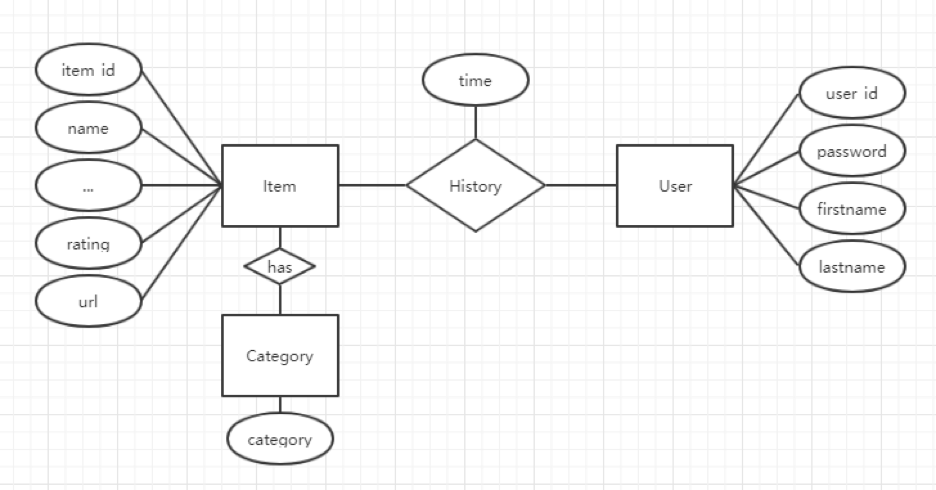
CREATE TABLE history (item_id, user_id, ,... FOREIGN KEY item_id REFERENCE item(item_id))users- store user information.
| User_id(primary key) | password | firstname | lastname |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1111 | abcd | Rick | Sun |
| 2222 | efgh | Matt | Yan |
items- store item information.
| item_id(primary key) | name | rating | url |
|---|---|---|---|
| abcd | event1 | 5 | www.example1.com |
| efgh | event1 | 0 | www.example2.com |
category- store item-category relationship
It’s an implementation detail, we could save category in item table, but there will be more string join/split manipulations in our code, so let’s save them in a separate table.
| item_id | category |
|---|---|
| abcd | party |
| efgh | party |
| efgh | sports |
Set item_id and category both as Primary Key, to map multiple items to multiple items.
history- store user favorite history
| User_id(foreign key) => user(user_id) | item_id | time |
|---|---|---|
| 1111 | abcd | 01/01/2018 |
| 1111 | efgh | 01/02/2018 |
| 2222 | efgh | 01/03/2018 |
A few more concept:
Unique key: a key in a relational database that is unique for each record.Primary key: Also a key that is unique for each record. Cannot be NULL and used as a unique identifier.Foreign key: a key used to link two tables together. A FOREIGN KEY is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that refers to the PRIMARY KEY in another table.Index: improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. MySQL will create index on column which is declared as key.
SQL
- SEQUEL (Structured English QUEry Language)
Structured Query Language is a programming language, which is used to communicate with DBMS. The standard language for relational DBMS.
Create tables in Java program
Connect to database from our Java program by JDBC
Just like our Java servlet classes. JDBC provides interfaces and classes for writing database operations. Technically speaking, JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is a standard API that defines how Java programs access database management systems. Since JDBC is a standard specification, one Java program that uses the JDBC API can connect to any database management system (DBMS), as long as a driver exists for that particular DBMS.
- download JDBC archive from http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/
- add the .jar file into your Eclipse lib. You can drag .jar file to WebContent/WEB-INF/lib directly, or copy that file and paste it (if it does not exist).
- For DB related functions, please always use:
import java.sql.xxx;
Create our db related package
create a new package named
db, then add a new interface calledDBConnection. Will add support toMySQLandMongoDBlater.Add the basic function signature
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84public interface DBConnection {
/**
* Close the connection.
*/
public void close();
/**
* Insert the favorite items for a user.
*
* @param userId
* @param itemIds
*/
public void setFavoriteItems(String userId, List<String> itemIds);
/**
* Delete the favorite items for a user.
*
* @param userId
* @param itemIds
*/
public void unsetFavoriteItems(String userId, List<String> itemIds);
/**
* Get the favorite item id for a user.
*
* @param userId
* @return itemIds
*/
public Set<String> getFavoriteItemIds(String userId);
/**
* Get the favorite items for a user.
*
* @param userId
* @return items
*/
public Set<Item> getFavoriteItems(String userId);
/**
* Gets categories based on item id
*
* @param itemId
* @return set of categories
*/
public Set<String> getCategories(String itemId);
/**
* Search items near a geolocation and a term (optional).
*
* @param userId
* @param lat
* @param lon
* @param term
* (Nullable)
* @return list of items
*/
public List<Item> searchItems(double lat, double lon, String term);
/**
* Save item into db.
*
* @param item
*/
public void saveItem(Item item);
/**
* Get full name of a user. (This is not needed for main course, just for demo
* and extension).
*
* @param userId
* @return full name of the user
*/
public String getFullname(String userId);
/**
* Return whether the credential is correct. (This is not needed for main
* course, just for demo and extension)
*
* @param userId
* @param password
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean verifyLogin(String userId, String password);
}Create a concrete class
DBConnectionFactory, this class is used to createdbinstance1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class DBConnectionFactory {
// This should change based on the pipeline.
private static final String DEFAULT_DB = "mysql";
public static DBConnection getConnection(String db) {
switch (db) {
case "mysql":
// return new MySQLConnection();
return null;
case "mongodb":
// return new MongoDBConnection();
return null;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid db: " + db);
}
}
public static DBConnection getConnection() {
return getConnection(DEFAULT_DB);
}
}
create MySQL version of DBConnection implementation
create another package
db.mysql, which will only contains mysql version of DBConnection implementation. Then createMySQLDBUtilclass indb.mysqlpackage.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class MySQLDBUtil {
private static final String HOSTNAME = "localhost";
private static final String PORT_NUM = "8889"; // change it to your mysql port number
public static final String DB_NAME = "myproject";
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "root";
public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://"
+ HOSTNAME + ":" + PORT_NUM + "/" + DB_NAME
+ "?user=" + USERNAME + "&password=" + PASSWORD
+ "&autoReconnect=true&serverTimezone=UTC";
//jdbc:mysql://localhost:8889/myproject?user=root&password=root&autoReconnect=true&serverTimezone=UTC
}create a new class called
MySQLTableCreationto automatically reset our tables in our database. So in the future, you can run this function every time when you think the data stored in you DB is messed up.first let’s try to connect to MySQL through JDBC connection. Be careful, always use java.sql.* when eclipse ask you to import DB related packages.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27public class MySQLTableCreation {
// Run this as Java application to reset db schema.
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// This is java.sql.Connection. Not com.mysql.jdbc.Connection.
Connection conn = null;
// Step 1 Connect to MySQL.
try {
System.out.println("Connecting to " + MySQLDBUtil.URL);
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").getConstructor().newInstance();
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(MySQLDBUtil.URL);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (conn == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println("Import is done successfully.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Question: What does this do Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”).newInstance()?
Answer: Ensure the driver is registered. We useClass.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").getConstructor().newInstance();to registerjdbc.Driverclass toDriverManager, then create an instance of it usingconn = DriverManager.getConnection(MySQLDBUtil.URL);此处为反射机制的应用
after connect to MySQL, let’s try to drop old tables if they’re existed.
Syntax:DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table_name;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// Step 2 Drop tables in case they exist.
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS categories";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS history";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS items";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);create 4 tables: User, Item, Category, History. Syntax:
1
2
3
4
5
6CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
....
);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35// Step 3 Create new tables
sql = "CREATE TABLE items ("
+ "item_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "name VARCHAR(255),"
+ "rating FLOAT,"
+ "address VARCHAR(255),"
+ "image_url VARCHAR(255),"
+ "url VARCHAR(255),"
+ "distance FLOAT,"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (item_id))";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "CREATE TABLE categories ("
+ "item_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "category VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (item_id, category),"
+ "FOREIGN KEY (item_id) REFERENCES items(item_id))";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "CREATE TABLE users ("
+ "user_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "first_name VARCHAR(255),"
+ "last_name VARCHAR(255),"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (user_id))";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "CREATE TABLE history ("
+ "user_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "item_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,"
+ "last_favor_time TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (user_id, item_id),"
+ "FOREIGN KEY (item_id) REFERENCES items(item_id),"
+ "FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(user_id))";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
VarChar 指的是变长数组
last_favor_time TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP指的是如果没有给值,默认用当前时间填充
com.mysql.jdbc.Driveris deprecated, change tocom.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
Add a fake user. We don’t have register function in our application, so let’s create a user in our database. Syntax:
1
2INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);1
2
3
4
5// Step 4: insert data
sql = "INSERT INTO users VALUES ("
+ "'1111', '3229c1097c00d497a0fd282d586be050', 'John', 'Smith')";
System.out.println("Executing query: " + sql);
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);